Yusuf Ozturk has designed an elaborate PowerShell script that allows you to visually meter the resource utilization of your Hyper-V virtual machines in a web browser. This tool works even if your hosts are running CORE or GUI Hyper-V Server, as it relies on PoSHServer instead of IIS
Read more: http://www.altaro.com/hyper-v/hyper-v-resource-metering-using-poshstats-free-tool/#ixzz2Uhi80l3u
this is really cool stuff
If you want a pay for product you can check out 5nine Cloud Monitor for Hyper-V ver. 1.3 at
http://5nine.com/5nine-hyper-v-cloud-vMonitor.aspx
Tips, Tricks and Workarounds for the new free Microsoft core server 2012 or hyper-v 3.0 standalone server.
Wednesday, May 29, 2013
Wednesday, May 22, 2013
Free Script: Network Team and Virtual Switch Manipulation for Hyper-V 2012
This has now been added to pshvm.codeplex.com a free powershell hyper-v manager project.
Free Script: Network Team and Virtual Switch Manipulation for Hyper-V 2012
On 05.21.13, In Hyper-V Scripts & Tools (Free), by Eric
Siron
I’ve designed a PowerShell script to help you with network team and virtual switch management in Hyper-V Server 2012. It will also work for Windows Server 2012.
Download the script file: SwitchesAndTeams
This will work whether or not you have a GUI version of Windows Server 2012
or if it’s Hyper-V Server 2012.Features
- Create and delete network teams
- Set IP information on the primary team adapter
- Create and delete virtual switches
- Create and delete virtual adapters
- Set IP information on management OS virtual adapters
- Set the VLAN ID for management OS virtual adapters
Read more: http://www.altaro.com/hyper-v/free-script-network-team-and-virtual-switch-manipulation-for-hyper-v-2012/#ixzz2U1z5zpXl
Wednesday, May 15, 2013
Web interface to hyper-v 3.0 ... limited but works (Alpha)
http://www.blinkov.com/blog.html
Currently program allows only basic virtual machine management:
Start
Pause
Save
Shutdown
Turn off power
It is console application. It can work directly from command line on even on Hyper-V Server and support installation as service. Inside the application he placed a web server which hosts small web applications which handles calls to the virtual machines on a local Hyper-V server.
System requirements for host system: Hyper-V 3.0
Hyper-V Server 2012, Windows 2012 Server with Hyper-V role, Windows 8 with Hyper-V role.
Not Bad I see real potential if it progresses.
Currently program allows only basic virtual machine management:
Start
Pause
Save
Shutdown
Turn off power
It is console application. It can work directly from command line on even on Hyper-V Server and support installation as service. Inside the application he placed a web server which hosts small web applications which handles calls to the virtual machines on a local Hyper-V server.
System requirements for host system: Hyper-V 3.0
Hyper-V Server 2012, Windows 2012 Server with Hyper-V role, Windows 8 with Hyper-V role.
Not Bad I see real potential if it progresses.
Thursday, May 9, 2013
How to: Virtual-to-Physical Conversions (V2P)
Ok this is way cool and I liked the way they wrote this up so much I am just going to point you to them
So that load you thought would be fine on a hypervisor just didn’t work out, eh? Maybe it was just too intensive, or maybe your software vendor bumped you off support. Whatever the reason, the need for V2P happens. It’s not the easiest thing in the world, but it can be done. This article is written with Hyper-V Server in mind, but most of its guidance should be applicable regardless of hypervisor.
Read more: http://www.altaro.com/hyper-v/virtual-to-physical-conversions-v2p/#ixzz2SoxpeI7q
This is from the Altaro blog http://www.altaro.com/hyper-v/ this is worth book marking.
So that load you thought would be fine on a hypervisor just didn’t work out, eh? Maybe it was just too intensive, or maybe your software vendor bumped you off support. Whatever the reason, the need for V2P happens. It’s not the easiest thing in the world, but it can be done. This article is written with Hyper-V Server in mind, but most of its guidance should be applicable regardless of hypervisor.
Read more: http://www.altaro.com/hyper-v/virtual-to-physical-conversions-v2p/#ixzz2SoxpeI7q
This is from the Altaro blog http://www.altaro.com/hyper-v/ this is worth book marking.
So you want to find out the hyper-v host of VM from the VM desktop....
Easy just use regedit to browse to
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Virtual Machine\Guest\Parameters
"HostName"="VHOST1.mydomain"
"HostingSystemEditionId"=dword:00000008
"HostingSystemOsMajor"=dword:00000006
"HostingSystemOsMinor"=dword:00000002
"HostingSystemProcessorArchitecture"=dword:00000009
"HostingSystemSpMajor"=dword:00000000
"HostingSystemSpMinor"=dword:00000000
"PhysicalHostName"="VHOST1"
"PhysicalHostNameFullyQualified"="VHOST1.mydomain"
"VirtualMachineId"="B0C0B158-169D-40C9-B021-726858DBAF82"
"VirtualMachineName"="TESTVM1"
And there you have it, useful if you have multiple Vhosts and someone moved something and forgot to document where.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Virtual Machine\Guest\Parameters
"HostName"="VHOST1.mydomain"
"HostingSystemEditionId"=dword:00000008
"HostingSystemOsMajor"=dword:00000006
"HostingSystemOsMinor"=dword:00000002
"HostingSystemProcessorArchitecture"=dword:00000009
"HostingSystemSpMajor"=dword:00000000
"HostingSystemSpMinor"=dword:00000000
"PhysicalHostName"="VHOST1"
"PhysicalHostNameFullyQualified"="VHOST1.mydomain"
"VirtualMachineId"="B0C0B158-169D-40C9-B021-726858DBAF82"
"VirtualMachineName"="TESTVM1"
And there you have it, useful if you have multiple Vhosts and someone moved something and forgot to document where.
Nice listing of Hyper-V tools and Powershell Scripts that you may find useful... Way to go Microsoft Technet
Yeap, even some of my posts are linked here.
pshvm.codeplex.com my master piece a free powershell hyper-v manager project.
Hyper-V: Tools from Microsoft Technet
Altaro Backup Blog Tons of good postings
Hyper-V Servers Best Practices and checklist This is worth the read
Hyper-V Forum -Official Microsoft Technet Site
pshvm.codeplex.com my master piece a free powershell hyper-v manager project.
Hyper-V: Tools from Microsoft Technet
Hyper-V: Scripts from Microsoft Technet
I have found some of the links very useful and some of them not so much.
CODEPLEX CodePlex is Microsoft's free open source project hosting site.
Hyper-V Servers Best Practices and checklist This is worth the read
Hyper-V Forum -Official Microsoft Technet Site
Monday, May 6, 2013
Using powershell to get a detailed report of your hyper-v Server and VM's running on it
This is now officially a free part of microsofts Codeplex project at reporting.codeplex.com- Yeah!
This has now been added to pshvm.codeplex.com a free GUI powershell hyper-v manager.
NEW******************NEW*********************NEW*****************NEW
Just released a new hyper-v manager that is free for non commercial use and pay for use if commercial.
I endorse this product as I helped in it's design and features and the GUI is much better than my product.
http://www.probus-it.se/hypervtools/hypervmanager
Probus-IT Hyper-V Manager (HVM) will help you to manage Hyper-V Servers and virtual machines. It is especially useful on core installations where you cannot run Microsoft Hyper-V manager locally. No RSAT or DOT-Net install needed. No fiddling with cmdkey and HVRemote-scripts. Installs on 32 and 64-Bit windows. Use it on Servers, desktops and Core installations both 32 and 64-Bit.
Thanks Håkan Lindén
NEW******************NEW*********************NEW*****************NEW
Single Powershell script to get a detailed report of your Vhosts and its VM's , works in Core and Datacenter 2012 versions running powershell 3.0. You can kick it off with a batch file see below or simply right-click on it and choose run with powershell if you have a GUI desktop.
Create directory structure C:\software\reports
save the below 2 lines as getreport.bat and save to C:\software then sent to desktop as link.
call powershell C:\software\getvmlist.ps1
exit
Save the below as getvmreport.ps1 to C:\software\
if you want to download them go to https://reporting.codeplex.com/releases/view/108006
Contents of getvmlist.ps1
ECHO "RUNNING THE REPORT NOW...takes approximately 2 minutes"
# Variables
$DateStamp = get-date -uformat "%m-%d-%Y"
# path and filename for report file
$file = "C:\software\reports\Report_$DATEStamp.txt"
$VMS = get-vm
$computers = $Env:COMPUTERNAME
# put todays date and time in the file
echo "Date report was ran" | out-file $file
get-date | out-file $file -append
# get the vhost uptime
Get-CimInstance Win32_OperatingSystem -comp $computers | Select @{Name="VHostName";Expression={$_."csname"}},@{Name="Uptime=D.H:M:S.Millseconds";Expression={(Get-Date) - $_.LastBootUpTime}},LastBootUpTime | format-table -autosize | out-file $file -append
# get the vhost name, total virtual CPU count, total RAM, virtualharddiskpath and virtualmachinepath
Get-VMHost | Select @{Name="VHostName";Expression={$_."Name"}},@{N="Total RAM(GB)";E={""+ [math]::round($_.Memorycapacity/1GB)}},logicalprocessorcount,virtualharddiskpath,virtualmachinepath | format-table -autosize | out-file $file -append
echo "VHOST Server IP Addresses and NIC's" | out-file $file -append
Get-WMIObject win32_NetworkAdapterConfiguration | Where-Object { $_.IPEnabled -eq $true } | Select IPAddress,Description | format-table -autosize | out-file $file -append
echo "VHOST Server drive C: Disk Space" | out-file $file -append
# to get D: drive add ,D after C - E: drive ,E etc.
Get-psdrive C | Select Root,@{N="Total(GB)";E={""+ [math]::round(($_.free+$_.used)/1GB)}},@{N="Used(GB)";E={""+ [math]::round($_.used/1GB)}},@{N="Free(GB)";E={""+ [math]::round($_.free/1GB)}} |format-table -autosize | out-file $file -append
echo "VHosts virtual switch(s) information" | out-file $file -append
get-vmswitch * | out-file $file -append
echo "Total number of VM's on server" | out-file $file -append
echo "------------------------------" | out-file $file -append
$VMS.Count | out-file $file -append
echo " " | out-file $file -append
echo "NOTE: Nothing listed under DVD Media Path = Nothing mounted in DVD" | out-file $file -append
$outputArray = @()
foreach($VM in $VMS)
{
$VMsRAM = [math]::round($VM.Memoryassigned/1GB)
$VMsCPU = $VM.processorCount
$VMsState = $VM.State
$VMsStatus = $VM.Status
$VMsUptime = $VM.Uptime
$VMsAutomaticstartaction = $VM.Automaticstartaction
$VMsIntegrationServicesVersion = $VM.IntegrationServicesVersion
$VMsReplicationState = $VM.ReplicationState
$VHDs = Get-VHD -VMId $VM.VMiD
$VHDsGB = [math]::round($VHDs.FileSize/1GB)
$VMDVD = Get-vmdvddrive -VMname $VM.VMname
$output = new-object psobject
$output | add-member noteproperty "VM Name" $VM.Name
$output | add-member noteproperty "RAM(GB)" $VMsRAM
$output | add-member noteproperty "vCPU" $VMsCPU
$output | add-member noteproperty "State" $VMsState
$output | add-member noteproperty "Status" $VMsStatus
$output | add-member noteproperty "Uptime" $VMsUptime
$output | add-member noteproperty "Start Action" $VMsAutomaticstartaction
$output | add-member noteproperty "Integration Tools" $VMsIntegrationServicesVersion
$output | add-member noteproperty "Replication State" $VMsReplicationState
$output | add-member noteproperty "VHD Path" $VHDs.Path
$output | add-member noteproperty "Size GB" $VHDsGB
$output | add-member noteproperty "VHD Type" $VHDs.vhdtype
$output | add-member noteproperty "VHD Format" $VHDs.vhdformat
$output | add-member noteproperty "DVD Media Type" $VMDVD.dvdmediatype
$output | add-member noteproperty "DVD Media Path" $VMDVD.path
$outputArray += $output
}
write-output $outputarray | sort "VM Name" | format-table * -autosize | out-string -width 600 | out-file $file -append
Echo "VM's BIOS setting" | out-file $file -append
get-vmbios * | sort "VMName" | Format-Table -autosize | out-file $file -append
echo "VM's Virtual Switch name and IP address" | out-file $file -append
get-vmnetworkadapter * | Select vmname,switchname,ipaddresses | sort "VMName" | format-table -autosize | out-file $file -append
echo "VM's Snapshot and location" | out-file $file -append
echo "If nothing is Listed below, then there are no Snapshots" | sort "VMName" | format-table -autosize | out-file $file -append
get-vmsnapshot -vmname * | out-file $file -append
#load the report in notepad
notepad.exe "C:\software\reports\Report_$DATEStamp.txt"
exit
Output of the report.bat to C:\softeware\reports\report_%date%.txt
Date report was ran
Thursday, May 23, 2013 2:27:52 PM
VHostName Uptime=D.H:M:S.Millseconds LastBootUpTime
--------- -------------------------- --------------
VHOST1 21.02:41:19.8376964 5/2/2013 11:46:32 AM
VHostName Total RAM(GB) LogicalProcessorCount VirtualHardDiskPath VirtualMachinePath
--------- ------------- --------------------- ------------------- ------------------
VHOST1 192 32 C:\VirtualServers C:\VirtualServers
VHOST Server IP Addresses and NIC's
IPAddress Description
--------- -----------
{10.1.104.10, fe80::5c8b:7bd6:cb53:2ccd} Hyper-V Virtual Ethernet Adapter #2
VHOST Server drive C: Disk Space
Root Total(GB) Used(GB) Free(GB)
---- --------- -------- --------
C:\ 1675 918 757
VHosts virtual switch(s) information
Name SwitchType NetAdapterInterfaceDescription
---- ---------- ------------------------------
PROD Network External Broadcom BCM5709C NetXtreme II GigE (NDIS VBD Client) #36
Total number of VM's on server
------------------------------
11
NOTE: Nothing listed under DVD Media Path = Nothing mounted in DVD
VM Name RAM(GB) vCPU State Status Uptime Start Action Integration Tools Replication State VHD Path Size GB VHD Type VHD Format DVD Media Type DVD Media Path
------- ------- ---- ----- ------ ------ ------------ ----------------- ----------------- -------- ------- -------- ---------- -------------- --------------
TEST1 2 1 Running Operating normally 8.11:18:28 StartIfRunning 6.2.9200.16384 Disabled C:\VirtualServers\Test1\test1-2008r2.vhdx 70 Fixed VHDX None
VM's BIOS setting
VMName StartupOrder NumLockEnabled
------ ------------ --------------
TEST1 {CD, IDE, LegacyNetworkAdapter, Floppy} True
VM's Virtual Switch name and IP address
VMName SwitchName IPAddresses
------ ---------- -----------
TEST1 PROD Network {10.1.100.5, fe80::8929:b7c0:6427:1b29}
VM's Snapshot and location
If nothing is Listed below, then there are no Snapshots
You now have a detailed report file that tells you the :
The Reports data and time
The Vhost's Name and Uptime
The Vhost's amount of RAM,Virtual CPUs,the virtual hard disk path and virtual machine path.
The Vhosts IP addresses, MACs and NIC Description
The Vhost disk space available on drive C: (you can add as many drives as you need in the script)
The Vhosts Virtual switches and their names
The Total # of VM's on the VHost and their: Name, RAM(GB), vCPU Count, State, Status, Uptime, AutomaticStartAction, IntegrationServicesVersion
The VM's BIOS setting (startorder and num-lock state)
*The VM's Virtual Switch it is attached to and IP address/MAC
The VM's DVD information and if anything is mounted
The VM's Hard drive file location, type, format and size
The VM's snapshots and location
* If you know for a fact your VM's have a NIC and IP address but the report shows none, you need to install the latest Microsoft Integration tools in order for the powershell scrip to see your VM's IP.
NOTE:
You can use the task scheduler i talked about in the backups blog post to autorun this during the day and them use a dos command line emailer to send you the file in email via smtp.
This has now been added to pshvm.codeplex.com a free GUI powershell hyper-v manager.
NEW******************NEW*********************NEW*****************NEW
Just released a new hyper-v manager that is free for non commercial use and pay for use if commercial.
I endorse this product as I helped in it's design and features and the GUI is much better than my product.
http://www.probus-it.se/hypervtools/hypervmanager
Probus-IT Hyper-V Manager (HVM) will help you to manage Hyper-V Servers and virtual machines. It is especially useful on core installations where you cannot run Microsoft Hyper-V manager locally. No RSAT or DOT-Net install needed. No fiddling with cmdkey and HVRemote-scripts. Installs on 32 and 64-Bit windows. Use it on Servers, desktops and Core installations both 32 and 64-Bit.
Thanks Håkan Lindén
NEW******************NEW*********************NEW*****************NEW
Single Powershell script to get a detailed report of your Vhosts and its VM's , works in Core and Datacenter 2012 versions running powershell 3.0. You can kick it off with a batch file see below or simply right-click on it and choose run with powershell if you have a GUI desktop.
Create directory structure C:\software\reports
save the below 2 lines as getreport.bat and save to C:\software then sent to desktop as link.
call powershell C:\software\getvmlist.ps1
exit
Save the below as getvmreport.ps1 to C:\software\
if you want to download them go to https://reporting.codeplex.com/releases/view/108006
Contents of getvmlist.ps1
ECHO "RUNNING THE REPORT NOW...takes approximately 2 minutes"
# Variables
$DateStamp = get-date -uformat "%m-%d-%Y"
# path and filename for report file
$file = "C:\software\reports\Report_$DATEStamp.txt"
$VMS = get-vm
$computers = $Env:COMPUTERNAME
# put todays date and time in the file
echo "Date report was ran" | out-file $file
get-date | out-file $file -append
# get the vhost uptime
Get-CimInstance Win32_OperatingSystem -comp $computers | Select @{Name="VHostName";Expression={$_."csname"}},@{Name="Uptime=D.H:M:S.Millseconds";Expression={(Get-Date) - $_.LastBootUpTime}},LastBootUpTime | format-table -autosize | out-file $file -append
# get the vhost name, total virtual CPU count, total RAM, virtualharddiskpath and virtualmachinepath
Get-VMHost | Select @{Name="VHostName";Expression={$_."Name"}},@{N="Total RAM(GB)";E={""+ [math]::round($_.Memorycapacity/1GB)}},logicalprocessorcount,virtualharddiskpath,virtualmachinepath | format-table -autosize | out-file $file -append
echo "VHOST Server IP Addresses and NIC's" | out-file $file -append
Get-WMIObject win32_NetworkAdapterConfiguration | Where-Object { $_.IPEnabled -eq $true } | Select IPAddress,Description | format-table -autosize | out-file $file -append
echo "VHOST Server drive C: Disk Space" | out-file $file -append
# to get D: drive add ,D after C - E: drive ,E etc.
Get-psdrive C | Select Root,@{N="Total(GB)";E={""+ [math]::round(($_.free+$_.used)/1GB)}},@{N="Used(GB)";E={""+ [math]::round($_.used/1GB)}},@{N="Free(GB)";E={""+ [math]::round($_.free/1GB)}} |format-table -autosize | out-file $file -append
echo "VHosts virtual switch(s) information" | out-file $file -append
get-vmswitch * | out-file $file -append
echo "Total number of VM's on server" | out-file $file -append
echo "------------------------------" | out-file $file -append
$VMS.Count | out-file $file -append
echo " " | out-file $file -append
echo "NOTE: Nothing listed under DVD Media Path = Nothing mounted in DVD" | out-file $file -append
$outputArray = @()
foreach($VM in $VMS)
{
$VMsRAM = [math]::round($VM.Memoryassigned/1GB)
$VMsCPU = $VM.processorCount
$VMsState = $VM.State
$VMsStatus = $VM.Status
$VMsUptime = $VM.Uptime
$VMsAutomaticstartaction = $VM.Automaticstartaction
$VMsIntegrationServicesVersion = $VM.IntegrationServicesVersion
$VMsReplicationState = $VM.ReplicationState
$VHDs = Get-VHD -VMId $VM.VMiD
$VHDsGB = [math]::round($VHDs.FileSize/1GB)
$VMDVD = Get-vmdvddrive -VMname $VM.VMname
$output = new-object psobject
$output | add-member noteproperty "VM Name" $VM.Name
$output | add-member noteproperty "RAM(GB)" $VMsRAM
$output | add-member noteproperty "vCPU" $VMsCPU
$output | add-member noteproperty "State" $VMsState
$output | add-member noteproperty "Status" $VMsStatus
$output | add-member noteproperty "Uptime" $VMsUptime
$output | add-member noteproperty "Start Action" $VMsAutomaticstartaction
$output | add-member noteproperty "Integration Tools" $VMsIntegrationServicesVersion
$output | add-member noteproperty "Replication State" $VMsReplicationState
$output | add-member noteproperty "VHD Path" $VHDs.Path
$output | add-member noteproperty "Size GB" $VHDsGB
$output | add-member noteproperty "VHD Type" $VHDs.vhdtype
$output | add-member noteproperty "VHD Format" $VHDs.vhdformat
$output | add-member noteproperty "DVD Media Type" $VMDVD.dvdmediatype
$output | add-member noteproperty "DVD Media Path" $VMDVD.path
$outputArray += $output
}
write-output $outputarray | sort "VM Name" | format-table * -autosize | out-string -width 600 | out-file $file -append
Echo "VM's BIOS setting" | out-file $file -append
get-vmbios * | sort "VMName" | Format-Table -autosize | out-file $file -append
echo "VM's Virtual Switch name and IP address" | out-file $file -append
get-vmnetworkadapter * | Select vmname,switchname,ipaddresses | sort "VMName" | format-table -autosize | out-file $file -append
echo "VM's Snapshot and location" | out-file $file -append
echo "If nothing is Listed below, then there are no Snapshots" | sort "VMName" | format-table -autosize | out-file $file -append
get-vmsnapshot -vmname * | out-file $file -append
#load the report in notepad
notepad.exe "C:\software\reports\Report_$DATEStamp.txt"
exit
Output of the report.bat to C:\softeware\reports\report_%date%.txt
Date report was ran
Thursday, May 23, 2013 2:27:52 PM
VHostName Uptime=D.H:M:S.Millseconds LastBootUpTime
--------- -------------------------- --------------
VHOST1 21.02:41:19.8376964 5/2/2013 11:46:32 AM
VHostName Total RAM(GB) LogicalProcessorCount VirtualHardDiskPath VirtualMachinePath
--------- ------------- --------------------- ------------------- ------------------
VHOST1 192 32 C:\VirtualServers C:\VirtualServers
VHOST Server IP Addresses and NIC's
IPAddress Description
--------- -----------
{10.1.104.10, fe80::5c8b:7bd6:cb53:2ccd} Hyper-V Virtual Ethernet Adapter #2
VHOST Server drive C: Disk Space
Root Total(GB) Used(GB) Free(GB)
---- --------- -------- --------
C:\ 1675 918 757
VHosts virtual switch(s) information
Name SwitchType NetAdapterInterfaceDescription
---- ---------- ------------------------------
PROD Network External Broadcom BCM5709C NetXtreme II GigE (NDIS VBD Client) #36
Total number of VM's on server
------------------------------
11
NOTE: Nothing listed under DVD Media Path = Nothing mounted in DVD
VM Name RAM(GB) vCPU State Status Uptime Start Action Integration Tools Replication State VHD Path Size GB VHD Type VHD Format DVD Media Type DVD Media Path
------- ------- ---- ----- ------ ------ ------------ ----------------- ----------------- -------- ------- -------- ---------- -------------- --------------
TEST1 2 1 Running Operating normally 8.11:18:28 StartIfRunning 6.2.9200.16384 Disabled C:\VirtualServers\Test1\test1-2008r2.vhdx 70 Fixed VHDX None
VM's BIOS setting
VMName StartupOrder NumLockEnabled
------ ------------ --------------
TEST1 {CD, IDE, LegacyNetworkAdapter, Floppy} True
VM's Virtual Switch name and IP address
VMName SwitchName IPAddresses
------ ---------- -----------
TEST1 PROD Network {10.1.100.5, fe80::8929:b7c0:6427:1b29}
VM's Snapshot and location
If nothing is Listed below, then there are no Snapshots
You now have a detailed report file that tells you the :
The Reports data and time
The Vhost's Name and Uptime
The Vhost's amount of RAM,Virtual CPUs,the virtual hard disk path and virtual machine path.
The Vhosts IP addresses, MACs and NIC Description
The Vhost disk space available on drive C: (you can add as many drives as you need in the script)
The Vhosts Virtual switches and their names
The Total # of VM's on the VHost and their: Name, RAM(GB), vCPU Count, State, Status, Uptime, AutomaticStartAction, IntegrationServicesVersion
The VM's BIOS setting (startorder and num-lock state)
*The VM's Virtual Switch it is attached to and IP address/MAC
The VM's DVD information and if anything is mounted
The VM's Hard drive file location, type, format and size
The VM's snapshots and location
* If you know for a fact your VM's have a NIC and IP address but the report shows none, you need to install the latest Microsoft Integration tools in order for the powershell scrip to see your VM's IP.
NOTE:
You can use the task scheduler i talked about in the backups blog post to autorun this during the day and them use a dos command line emailer to send you the file in email via smtp.
Using Powershell at logon to show you the VHOST and VM status... Brief detail
This has now been added to pshvm.codeplex.com a free powershell hyper-v manager project.
Ok create welcome.ps1 file that contains
# Variables
$DateStamp = get-date -uformat "%m-%d-%Y"
$computers = $Env:COMPUTERNAME
$VMS = get-vm
$file = "C:\software\reports\welcome.txt"
# Display a welcome message
echo "Log On Welcome Report" | out-file $file
get-date | out-file $file -append
# get the vhost uptime
Get-CimInstance Win32_OperatingSystem -comp $computers | Select @{Name="VHostName";Expression={$_."csname"}},@{Name="Uptime=D.H:M:S.Millseconds";Expression={(Get-Date) - $_.LastBootUpTime}},LastBootUpTime | format-table -autosize | out-file $file -append
echo "VHOST Server drive C: Disk Space" | out-file $file -append
# to get D: drive add ,D after C - E: drive ,E etc.
Get-psdrive C | Select Root,@{N="Total(GB)";E={""+ [math]::round(($_.free+$_.used)/1GB)}},@{N="Used(GB)";E={""+ [math]::round($_.used/1GB)}},@{N="Free(GB)";E={""+ [math]::round($_.free/1GB)}} |format-table -autosize | out-file $file -append
echo "Total number of VM's on server" | out-file $file -append
echo "------------------------------" | out-file $file -append
$VMS.Count | out-file $file -append
echo " " | out-file $file -append
write-host Current virtual machine status: | out-file $file -append
get-vm | out-file $file -append
notepad.exe "C:\software\reports\Welcome.txt"
exit
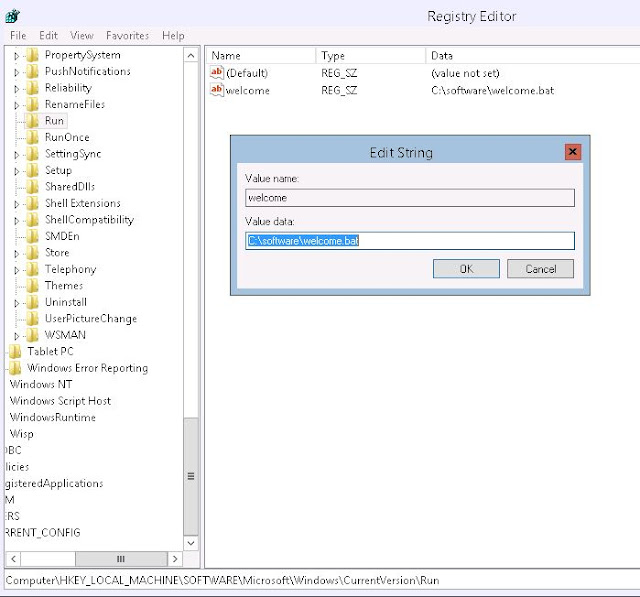
Now create a welcome.bat that contains
call powershell C:\software\welcome.ps1
Now edit the your registry:
Whenever you log onto the vhost you will get a brief report of the vhost and vm's like this in notepad.
Log On Welcome Report
Friday, May 31, 2013 4:45:12 PM
VHostName Uptime=D.H:M:S.Millseconds LastBootUpTime
--------- -------------------------- --------------
VHOST1 -18:57:23.6969442 6/1/2013 11:42:36 AM
VHOST Server drive C: Disk Space
Root Total(GB) Used(GB) Free(GB)
---- --------- -------- --------
C:\ 408 25 383
Total number of VM's on server
------------------------------
1
Name State CPUUsage(%) MemoryAssigned(M) Uptime Status
---- ----- ----------- ----------------- ------ ------
test1 Running 0 4096 00:45:27 Operating normally
Ok create welcome.ps1 file that contains
# Variables
$DateStamp = get-date -uformat "%m-%d-%Y"
$computers = $Env:COMPUTERNAME
$VMS = get-vm
$file = "C:\software\reports\welcome.txt"
# Display a welcome message
echo "Log On Welcome Report" | out-file $file
get-date | out-file $file -append
# get the vhost uptime
Get-CimInstance Win32_OperatingSystem -comp $computers | Select @{Name="VHostName";Expression={$_."csname"}},@{Name="Uptime=D.H:M:S.Millseconds";Expression={(Get-Date) - $_.LastBootUpTime}},LastBootUpTime | format-table -autosize | out-file $file -append
echo "VHOST Server drive C: Disk Space" | out-file $file -append
# to get D: drive add ,D after C - E: drive ,E etc.
Get-psdrive C | Select Root,@{N="Total(GB)";E={""+ [math]::round(($_.free+$_.used)/1GB)}},@{N="Used(GB)";E={""+ [math]::round($_.used/1GB)}},@{N="Free(GB)";E={""+ [math]::round($_.free/1GB)}} |format-table -autosize | out-file $file -append
echo "Total number of VM's on server" | out-file $file -append
echo "------------------------------" | out-file $file -append
$VMS.Count | out-file $file -append
echo " " | out-file $file -append
write-host Current virtual machine status: | out-file $file -append
get-vm | out-file $file -append
notepad.exe "C:\software\reports\Welcome.txt"
exit
Now create a welcome.bat that contains
call powershell C:\software\welcome.ps1
Now edit the your registry:
Whenever you log onto the vhost you will get a brief report of the vhost and vm's like this in notepad.
Log On Welcome Report
Friday, May 31, 2013 4:45:12 PM
VHostName Uptime=D.H:M:S.Millseconds LastBootUpTime
--------- -------------------------- --------------
VHOST1 -18:57:23.6969442 6/1/2013 11:42:36 AM
VHOST Server drive C: Disk Space
Root Total(GB) Used(GB) Free(GB)
---- --------- -------- --------
C:\ 408 25 383
Total number of VM's on server
------------------------------
1
Name State CPUUsage(%) MemoryAssigned(M) Uptime Status
---- ----- ----------- ----------------- ------ ------
test1 Running 0 4096 00:45:27 Operating normally
Wednesday, May 1, 2013
How to see what VM's have a DVD/ISO file mounted and how to mass unmount the DVD/ISO files
This has now been added to pshvm.codeplex.com a free powershell hyper-v manager project.
To find what vm's have a DVD/ISO mounted
From with Powershell typeTo find what vm's have a DVD/ISO mounted
get-vmdvddrive -vmname *
it will list like this
VMName ControllerType ControllerNumber ControllerLocation DvdMediaType Path
------ -------------- ---------------- ------------------ ------------ ----
TEST1 IDE 1 0 ISO C:\baseimages\WindowsS...
TEST IDE 1 0 None
To mass unmount/eject the DVD/ISO file
From with Powershell type
get-vmdvddrive -vmname * | set-vmdvddrive -path $null
it will list like this
VMName ControllerType ControllerNumber ControllerLocation DvdMediaType Path
------ -------------- ---------------- ------------------ ------------ ----
TEST1 IDE 1 0 None
TEST IDE 1 0 None
To add insert a DVD into a VM with Powershell:
To insert the MS Integration Tools ISO type (substitute tools ISO path for the ISO you wish to insert)
Set-VMDvdDrive -VMName Test1 -Path C:\Windows\system32\vmguest.iso
To eject any ISO from the DVD type
Set-VMDvdDrive -VMName Test1 -ControllerNumber 1 -ControllerLocation 0 -Path $null
Simple Powershell script to create a hyper-v VM
This has now been added to pshvm.codeplex.com a free powershell hyper-v manager project.
Updated 6/25/2013
This script will ask you questions and then builds the VM per your spec's / answers, unlike the one below this one will create a Fixed (Static) or Differencing (Dynamic) VHDx disk
$vswitch = get-vmswitch
$VPATH = get-vmhost
$VPATH | select virtualharddiskpath,virtualmachinepath | format-table -autosize
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "This script will walk you through creating a new VM with a Fixed or Dynamic Hard Disk"
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "!!! If you do not see any paths listed above, this process will fail !!!"
#Ask for input
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "-----------------------------------------------------------------"
$SelectedIndex = Read-Host "Type 0 to exit out of this Menu or Enter to Continue”
$Exit = $SelectedIndex
if($EXIT -eq 0)
{exit}
else {
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "Type in what is asked for: DO NOT USE ANY Quotes to frame answers"
$SelectedIndex1 = Read-Host "New VM Name (TEST1)"
$SelectedIndex2 = Read-Host "RAM in GB (2)"
$SelectedIndex3 = Read-Host "vCPU Count (4)"
$SelectedIndex6 = Read-Host "Virtual hard Disk Size (70GB)"
$SelectedIndex7 = Read-Host "OS ISO file path (C:\iso\2008r2sp1.iso)"
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" ""
$1 = "\"
$2 = ".vhdx"
$3 = "\"
$NAME = $SelectedIndex1
$Name1 = $Name
$RAM = [int64]$SelectedIndex2 * 1073741824
$vCPU = $SelectedIndex3
$PATHVM1 = ($VPATH.virtualmachinepath)
$PATHVM = ($PATHVM1 += $1 += $NAME)
$newVHDPATH1 = ($VPATH.virtualharddiskpath)
$newVHDPATH = ($newVHDPATH1 += $1 += $3 +=$NAME1 += $2)
$newVHDsize = [int64]$SelectedIndex6 * 1073741824
$PATHDVD = $SelectedIndex7
#Ask for disk type selection
Write-host -foreground "magenta" "1. Fixed = Static"
Write-host -foreground "magenta" "2. Differencing = Dynamic"
Write-host -foreground "yellow" "NOTE: this step can take several minutes if you choose Fixed"
$SelectedIndex9 = Read-Host "**** Please select a Number For type of VHDx Disk ***"
$Selection = $SelectedIndex9
if($Selection -eq 1)
{New-VHD -Fixed -Path $newVHDPATH -SizeBytes $newVHDsize}
elseif ($Selection -eq 2)
{New-VHD -Path $newVHDPATH -SizeBytes $newVHDsize}
# create numbered array of vswitches
$i = 1
$vswitch | ForEach-Object {
Write-Host "$i $($_.Name)”
$i++
}
#Ask for number selection
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" ""
$SelectedVMIndex = Read-Host "**** Please select a Number to attach the VM too ***”
$SelectedVMIndex = $SelectedVMIndex - 1
$SelectedVM = $vswitch[$SelectedVMIndex]
$vSwitch = $SelectedVM.name
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" ""
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "**** Input 1=Start-vm or Press Enter to Leave VM powered off ****"
$SelectedIndex8 = Read-Host "Type Selection”
$Power = $SelectedIndex8
NEW-VM –Name $NAME –MemoryStartupBytes $RAM -Path $PATHVM
#New-VHD -Path $newVHDPATH $Disktype -SizeBytes $newVHDsize
Add-VMHardDiskDrive -VMName $NAME -Path $newVHDPATH
Set-VMProcessor $NAME -Count $vCPU
get-vmnetworkadapter -vmname $NAME | connect-vmnetworkadapter -switchname $vSwitch
Set-VMBios $NAME -EnableNumlock
Set-VMDvdDrive -VMName $NAME -ControllerNumber 1 -ControllerLocation 0 –Path $PATHDVD
if($SelectedIndex8 -eq 1)
{start-vm "$Name"
cls
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "**** Virtual Machine $Name Status *****"
Write-Host -foreground "Yellow" "!!!! It shows $Name Status twice, the bottom one is the true STATE !!!!"
get-vm "$Name"}
else {
cls
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "**** Virtual Machine $Name is ready to be started ****"
get-vm "$Name"}
}
Updated 6/14/2013
This script will ask you questions and then build the VM per your spec's / answers however it only build a Differncing (dynamic) VHDx file
$vswitch = get-vmswitch
$VPATH = get-vmhost
$VPATH | select virtualharddiskpath,virtualmachinepath | format-table -autosize
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "This script will walk you through creating a new VM with a Dynamic Hard Disk"
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "!!! If you do not see any paths listed above, this process will fail !!!"
#Ask for input
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "-----------------------------------------------------------------"
$SelectedIndex = Read-Host "Type 0 to exit out of this Menu or Enter to Continue”
$Exit = $SelectedIndex
if($EXIT -eq 0)
{exit}
else {
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "Type in what is asked for: DO NOT USE ANY Quotes to frame answers"
$SelectedIndex1 = Read-Host "New VM Name (TEST1)"
$SelectedIndex2 = Read-Host "RAM in GB (2)"
$SelectedIndex3 = Read-Host "vCPU Count (4)"
$SelectedIndex6 = Read-Host "Virtual hard Disk Size in GB (70)"
$SelectedIndex7 = Read-Host "OS ISO file path (C:\iso\2008r2sp1.iso)"
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" ""
$1 = "\"
$2 = ".vhdx"
$3 = "\"
$NAME = $SelectedIndex1
$Name1 = $Name
$RAM = [int64]$SelectedIndex2 * 1073741824
$vCPU = $SelectedIndex3
$PATHVM1 = ($VPATH.virtualmachinepath)
$PATHVM = ($PATHVM1 += $1 += $NAME)
$newVHDPATH1 = ($VPATH.virtualharddiskpath)
$newVHDPATH = ($newVHDPATH1 += $1 += $3 +=$NAME1 += $2)
$newVHDsize = [int64]$SelectedIndex6 * 1073741824
$PATHDVD = $SelectedIndex7
# reate numbered array of vswitches
$i = 1
$vswitch | ForEach-Object {
Write-Host "$i $($_.Name)”
$i++
}
#Ask for number selection
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" ""
$SelectedVMIndex = Read-Host "**** Please select a Number to attach theVM too ***”
$SelectedVMIndex = $SelectedVMIndex - 1
$SelectedVM = $vswitch[$SelectedVMIndex]
$vSwitch = $SelectedVM.name
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" ""
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "**** Input 1=Start-vm or Press Enter to Leave VM powered off ****"
$SelectedIndex8 = Read-Host "Type Selection”
$Power = $SelectedIndex8
NEW-VM –Name $NAME –MemoryStartupBytes $RAM -Path $PATHVM –newVHDPath $newVHDPATH -newVHDsizebytes $newVHDsize
Set-VMProcessor $NAME -Count $vCPU
get-vmnetworkadapter -vmname $NAME | connect-vmnetworkadapter -switchname $vSwitch
Set-VMBios $NAME -EnableNumlock
Set-VMDvdDrive -VMName $NAME -ControllerNumber 1 -ControllerLocation 0 –Path $PATHDVD
if($SelectedIndex8 -eq 1)
{start-vm "$name"
get-vm "$name"
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "!!!! It shows the same server twice but the bottom one is the true state !!!!" }
else {
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "**** VM is ready to be started ****"
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" ""}
}
I created this in notepad and named it addvm.ps1 and saved it to C:\software
To run this script open powershell
type cd\
type cd software
type .\addvm.ps1
Simple Powershell script to create a VM with a existing VHDX disk file
# Variables
# Name of server in hyper-v
$NAME = "test"
# Amount RAM in GB
$RAM = 4GB
# Path to store VM config files
$PATH = "C:\VirtualServers\test"
# Path to an existing VM Harddrive file
$VHDPATH = "C:\VirtualServers\test\2008r2-70gb.vhdx"
# Number vCPU's
$CPU = 4
# Name of Virtual Switch for first NIC
$NETWORK1 = "prod network"
# Un rem below for name of virtual switch for second NIC
# $NETWORK2 =
# Set-VMBios = Num lock .... enabled = -EnableNumlock or disabled = -DisableNumLock
New-VM –Name $NAME –MemoryStartupBytes $RAM -Path $PATH –VHDPath $VHDPATH
Set-VMProcessor $NAME -Count $CPU
get-vmnetworkadapter -vmname $NAME | connect-vmnetworkadapter -switchname $NETWORK1
Set-VMBios $NAME -EnableNumlock
Simple Powershell script to create a VM with a new VHDX file and attach an ISO for OS installation
Note this will be a dynamic harddisk, if you wish to change this read below**
# Variables
## Name of server in hyper-v
$NAME = "test1"
## Amount RAM in GB
$RAM = 4GB
## Number vCPU's
$CPU = 4
## Path to store VM config files
$PATH = "C:\VirtualServers\test1"
## Path to the new VHDX VM hard drive file
$newVHDPATH = "C:\VirtualServers\test1\2008r2-70gb.vhdx"
## Size to make the VM hard drive
$newVHDsize =70GB
## Path to the DVD ISO for OS installation
$PATHDVD = C:\ISO\2008r2sp1.iso
## Name of Virtual Switch for first NIC
$NETWORK1 = "prod network"
# Un rem below for name of virtual switch for second NIC
# $NETWORK2 =
## Set-VMBios = Num lock .... enabled = -EnableNumlock or disabled = -DisableNumLock
New-VM –Name $NAME –MemoryStartupBytes $RAM -Path $PATH –newVHDPath $newVHDPATH -newVHDsizebytes $newVHDsize
Set-VMProcessor $NAME -Count $CPU
get-vmnetworkadapter -vmname $NAME | connect-vmnetworkadapter -switchname $NETWORK1
Set-VMBios $NAME -EnableNumlock
Set-VMDvdDrive -VMName $NAME –Path $PATHDVD -ControllerNumber 1
**
Here are your steps to converta dynamic harddisk vhdx file toa fixed or static sized vhdx file:
1. Power the VM Server off if it is running
2. From the server console, open the powershell window, type (substitute C:\temp\ for your path)
PS C:\> Convert-VHD –Path c:\test\test.vhdx –DestinationPath c:\test\test1.vhdx -VHDType Fixed
This will convert your dynamic VHDX file and make it Fixed or Static VHDX file. The -VHDType options are Fixed, Dynamic and Differencing.
3. in powershell (removes the path to the old dynamic vhdx)
Remove-VMHardDiskDrive -VMName Test1 –ControllerType IDE -ControllerNumber 0 -ControllerLocation 0
4. In powershell (adds the path to the new Fixed or Static sized vhdx)
Add-VMHardDiskDrive -VMName Test1 -Path C:\test\test1.vhdx
your are VM is ready to ps C:\>start-vm test1.
You might want to delete the old VHDX file unless you are not done with it unless you like to waste disk space.
If you are building a VM from scratch. (IE using the DVD ISO method) you will need to eject the OS ISO DVD once it is installed and insert the MS Integration Tools ISO to install them.
This is how you do that in Powershell:
To eject the current DVD/ISO file type
Set-VMDvdDrive -VMName Test1 -ControllerNumber 1 -ControllerLocation 0 -Path $null
To insert the MS Integration Tools ISO type
Set-VMDvdDrive -VMName Test1 -Path C:\Windows\system32\vmguest.iso
To eject the MS Integration Tools ISO once intsalled type
Set-VMDvdDrive -VMName Test1 -ControllerNumber 1 -ControllerLocation 0 -Path $null
Updated 6/25/2013
This script will ask you questions and then builds the VM per your spec's / answers, unlike the one below this one will create a Fixed (Static) or Differencing (Dynamic) VHDx disk
$vswitch = get-vmswitch
$VPATH = get-vmhost
$VPATH | select virtualharddiskpath,virtualmachinepath | format-table -autosize
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "This script will walk you through creating a new VM with a Fixed or Dynamic Hard Disk"
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "!!! If you do not see any paths listed above, this process will fail !!!"
#Ask for input
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "-----------------------------------------------------------------"
$SelectedIndex = Read-Host "Type 0 to exit out of this Menu or Enter to Continue”
$Exit = $SelectedIndex
if($EXIT -eq 0)
{exit}
else {
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "Type in what is asked for: DO NOT USE ANY Quotes to frame answers"
$SelectedIndex1 = Read-Host "New VM Name (TEST1)"
$SelectedIndex2 = Read-Host "RAM in GB (2)"
$SelectedIndex3 = Read-Host "vCPU Count (4)"
$SelectedIndex6 = Read-Host "Virtual hard Disk Size (70GB)"
$SelectedIndex7 = Read-Host "OS ISO file path (C:\iso\2008r2sp1.iso)"
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" ""
$1 = "\"
$2 = ".vhdx"
$3 = "\"
$NAME = $SelectedIndex1
$Name1 = $Name
$RAM = [int64]$SelectedIndex2 * 1073741824
$vCPU = $SelectedIndex3
$PATHVM1 = ($VPATH.virtualmachinepath)
$PATHVM = ($PATHVM1 += $1 += $NAME)
$newVHDPATH1 = ($VPATH.virtualharddiskpath)
$newVHDPATH = ($newVHDPATH1 += $1 += $3 +=$NAME1 += $2)
$newVHDsize = [int64]$SelectedIndex6 * 1073741824
$PATHDVD = $SelectedIndex7
#Ask for disk type selection
Write-host -foreground "magenta" "1. Fixed = Static"
Write-host -foreground "magenta" "2. Differencing = Dynamic"
Write-host -foreground "yellow" "NOTE: this step can take several minutes if you choose Fixed"
$SelectedIndex9 = Read-Host "**** Please select a Number For type of VHDx Disk ***"
$Selection = $SelectedIndex9
if($Selection -eq 1)
{New-VHD -Fixed -Path $newVHDPATH -SizeBytes $newVHDsize}
elseif ($Selection -eq 2)
{New-VHD -Path $newVHDPATH -SizeBytes $newVHDsize}
# create numbered array of vswitches
$i = 1
$vswitch | ForEach-Object {
Write-Host "$i $($_.Name)”
$i++
}
#Ask for number selection
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" ""
$SelectedVMIndex = Read-Host "**** Please select a Number to attach the VM too ***”
$SelectedVMIndex = $SelectedVMIndex - 1
$SelectedVM = $vswitch[$SelectedVMIndex]
$vSwitch = $SelectedVM.name
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" ""
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "**** Input 1=Start-vm or Press Enter to Leave VM powered off ****"
$SelectedIndex8 = Read-Host "Type Selection”
$Power = $SelectedIndex8
NEW-VM –Name $NAME –MemoryStartupBytes $RAM -Path $PATHVM
#New-VHD -Path $newVHDPATH $Disktype -SizeBytes $newVHDsize
Add-VMHardDiskDrive -VMName $NAME -Path $newVHDPATH
Set-VMProcessor $NAME -Count $vCPU
get-vmnetworkadapter -vmname $NAME | connect-vmnetworkadapter -switchname $vSwitch
Set-VMBios $NAME -EnableNumlock
Set-VMDvdDrive -VMName $NAME -ControllerNumber 1 -ControllerLocation 0 –Path $PATHDVD
if($SelectedIndex8 -eq 1)
{start-vm "$Name"
cls
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "**** Virtual Machine $Name Status *****"
Write-Host -foreground "Yellow" "!!!! It shows $Name Status twice, the bottom one is the true STATE !!!!"
get-vm "$Name"}
else {
cls
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "**** Virtual Machine $Name is ready to be started ****"
get-vm "$Name"}
}
Updated 6/14/2013
This script will ask you questions and then build the VM per your spec's / answers however it only build a Differncing (dynamic) VHDx file
$vswitch = get-vmswitch
$VPATH = get-vmhost
$VPATH | select virtualharddiskpath,virtualmachinepath | format-table -autosize
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "This script will walk you through creating a new VM with a Dynamic Hard Disk"
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "!!! If you do not see any paths listed above, this process will fail !!!"
#Ask for input
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "-----------------------------------------------------------------"
$SelectedIndex = Read-Host "Type 0 to exit out of this Menu or Enter to Continue”
$Exit = $SelectedIndex
if($EXIT -eq 0)
{exit}
else {
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "Type in what is asked for: DO NOT USE ANY Quotes to frame answers"
$SelectedIndex1 = Read-Host "New VM Name (TEST1)"
$SelectedIndex2 = Read-Host "RAM in GB (2)"
$SelectedIndex3 = Read-Host "vCPU Count (4)"
$SelectedIndex6 = Read-Host "Virtual hard Disk Size in GB (70)"
$SelectedIndex7 = Read-Host "OS ISO file path (C:\iso\2008r2sp1.iso)"
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" ""
$1 = "\"
$2 = ".vhdx"
$3 = "\"
$NAME = $SelectedIndex1
$Name1 = $Name
$RAM = [int64]$SelectedIndex2 * 1073741824
$vCPU = $SelectedIndex3
$PATHVM1 = ($VPATH.virtualmachinepath)
$PATHVM = ($PATHVM1 += $1 += $NAME)
$newVHDPATH1 = ($VPATH.virtualharddiskpath)
$newVHDPATH = ($newVHDPATH1 += $1 += $3 +=$NAME1 += $2)
$newVHDsize = [int64]$SelectedIndex6 * 1073741824
$PATHDVD = $SelectedIndex7
# reate numbered array of vswitches
$i = 1
$vswitch | ForEach-Object {
Write-Host "$i $($_.Name)”
$i++
}
#Ask for number selection
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" ""
$SelectedVMIndex = Read-Host "**** Please select a Number to attach theVM too ***”
$SelectedVMIndex = $SelectedVMIndex - 1
$SelectedVM = $vswitch[$SelectedVMIndex]
$vSwitch = $SelectedVM.name
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" ""
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "**** Input 1=Start-vm or Press Enter to Leave VM powered off ****"
$SelectedIndex8 = Read-Host "Type Selection”
$Power = $SelectedIndex8
NEW-VM –Name $NAME –MemoryStartupBytes $RAM -Path $PATHVM –newVHDPath $newVHDPATH -newVHDsizebytes $newVHDsize
Set-VMProcessor $NAME -Count $vCPU
get-vmnetworkadapter -vmname $NAME | connect-vmnetworkadapter -switchname $vSwitch
Set-VMBios $NAME -EnableNumlock
Set-VMDvdDrive -VMName $NAME -ControllerNumber 1 -ControllerLocation 0 –Path $PATHDVD
if($SelectedIndex8 -eq 1)
{start-vm "$name"
get-vm "$name"
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "!!!! It shows the same server twice but the bottom one is the true state !!!!" }
else {
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" "**** VM is ready to be started ****"
Write-Host -foreground "magenta" ""}
}
The above } is the end of the script
This method works the same but you have to edit file each time you want to create a VM.
I created this in notepad and named it addvm.ps1 and saved it to C:\software
To run this script open powershell
type cd\
type cd software
type .\addvm.ps1
Simple Powershell script to create a VM with a existing VHDX disk file
# Variables
# Name of server in hyper-v
$NAME = "test"
# Amount RAM in GB
$RAM = 4GB
# Path to store VM config files
$PATH = "C:\VirtualServers\test"
# Path to an existing VM Harddrive file
$VHDPATH = "C:\VirtualServers\test\2008r2-70gb.vhdx"
# Number vCPU's
$CPU = 4
# Name of Virtual Switch for first NIC
$NETWORK1 = "prod network"
# Un rem below for name of virtual switch for second NIC
# $NETWORK2 =
# Set-VMBios = Num lock .... enabled = -EnableNumlock or disabled = -DisableNumLock
New-VM –Name $NAME –MemoryStartupBytes $RAM -Path $PATH –VHDPath $VHDPATH
Set-VMProcessor $NAME -Count $CPU
get-vmnetworkadapter -vmname $NAME | connect-vmnetworkadapter -switchname $NETWORK1
Set-VMBios $NAME -EnableNumlock
Simple Powershell script to create a VM with a new VHDX file and attach an ISO for OS installation
Note this will be a dynamic harddisk, if you wish to change this read below**
# Variables
## Name of server in hyper-v
$NAME = "test1"
## Amount RAM in GB
$RAM = 4GB
## Number vCPU's
$CPU = 4
## Path to store VM config files
$PATH = "C:\VirtualServers\test1"
## Path to the new VHDX VM hard drive file
$newVHDPATH = "C:\VirtualServers\test1\2008r2-70gb.vhdx"
## Size to make the VM hard drive
$newVHDsize =70GB
## Path to the DVD ISO for OS installation
$PATHDVD = C:\ISO\2008r2sp1.iso
## Name of Virtual Switch for first NIC
$NETWORK1 = "prod network"
# Un rem below for name of virtual switch for second NIC
# $NETWORK2 =
## Set-VMBios = Num lock .... enabled = -EnableNumlock or disabled = -DisableNumLock
New-VM –Name $NAME –MemoryStartupBytes $RAM -Path $PATH –newVHDPath $newVHDPATH -newVHDsizebytes $newVHDsize
Set-VMProcessor $NAME -Count $CPU
get-vmnetworkadapter -vmname $NAME | connect-vmnetworkadapter -switchname $NETWORK1
Set-VMBios $NAME -EnableNumlock
Set-VMDvdDrive -VMName $NAME –Path $PATHDVD -ControllerNumber 1
**
Here are your steps to converta dynamic harddisk vhdx file toa fixed or static sized vhdx file:
1. Power the VM Server off if it is running
2. From the server console, open the powershell window, type (substitute C:\temp\ for your path)
PS C:\> Convert-VHD –Path c:\test\test.vhdx –DestinationPath c:\test\test1.vhdx -VHDType Fixed
This will convert your dynamic VHDX file and make it Fixed or Static VHDX file. The -VHDType options are Fixed, Dynamic and Differencing.
3. in powershell (removes the path to the old dynamic vhdx)
Remove-VMHardDiskDrive -VMName Test1 –ControllerType IDE -ControllerNumber 0 -ControllerLocation 0
4. In powershell (adds the path to the new Fixed or Static sized vhdx)
Add-VMHardDiskDrive -VMName Test1 -Path C:\test\test1.vhdx
your are VM is ready to ps C:\>start-vm test1.
You might want to delete the old VHDX file unless you are not done with it unless you like to waste disk space.
If you are building a VM from scratch. (IE using the DVD ISO method) you will need to eject the OS ISO DVD once it is installed and insert the MS Integration Tools ISO to install them.
This is how you do that in Powershell:
To eject the current DVD/ISO file type
Set-VMDvdDrive -VMName Test1 -ControllerNumber 1 -ControllerLocation 0 -Path $null
To insert the MS Integration Tools ISO type
Set-VMDvdDrive -VMName Test1 -Path C:\Windows\system32\vmguest.iso
To eject the MS Integration Tools ISO once intsalled type
Set-VMDvdDrive -VMName Test1 -ControllerNumber 1 -ControllerLocation 0 -Path $null
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)